Thank you for visiting this website although all articles written in Japanese only. This is the first greeting in English.
This website lists the titles of all local miss and local promotion girls(boys) in Japan. This is the first website covers all “public” local miss pageants and promotion girls in Japan, and the only website so far since 2015.
But note that it is limited to those recruited, selected, and appointed by highly public organizations.

We are not sure that the words “public miss pageant” is correct, anyway this website only list thats public. And the miss pageants organized by pure private companies are excluded.
So what are the “highly public organizations”?
We determined as follows.

These “APPLICABLE” organizations are “highly public organizations” we defined in this website.
1. Municipal/Prefecture level local governments
Local governments of municipalities (cities, towns, villages) and prefectures.
basis law = Local Autonomy Act (ja)地方自治法
2. Convention & Visitors Bureau (CVB)
In some of the cities, an organization to promote convention business (Convention Bureau) and the Tourism Association(s) are merged then organized as a CVB.
Most CVBs are joint ventures consisting of local governments, CCIs, and tourism associations.
basis law = none. so legal personality (and its name) varies and is not constant.
3. Tourism(Tourist/Visitors) Association(Bureau) (TA, TB, VA, VB, ..) or Destination Marketing/Management Organization (DMO)
The associations often acquire and execute the local gov’s tourism budget.
In small municipals with undeveloped tourist attractions, the local gov’s tourism section often doubles as the secretariat of the tourism association.
basis law = none. so legal personality (and its name) varies and is not constant.
4. Societies of Commerce and Industry (SCI)
Member companies of SCI are smaller than that of CCI in general.
basis law = Commerce and Industry Association Act (ja)商工会法
5. Chamber of Commerce and Industry (CCI)
basis law = Chambers of Commerce and Industry Act (ja)商工会議所法
6. Convention Bureau (CB)
A foundation or incorporated association organized to promote the convention business. The main member of CB is CCI for most CBs.
basis law = none.
In many cities, CB merged with tourism associations to become CVB.
7. Agricultural Cooperatives (Japan Agricultural Cooperatives = JA, Japan Fisheries Cooperatives = JF)
The prefecture level federations of JA/JFs (such as JA Zen-noh) are also applicable.
c.f. JA ZENCHU website
basis law = Agricultural Cooperatives Act (ja)農業協同組合法, Fishery Cooperatives Act (ja)水産業協同組合法, *Forestry Cooperative Act (ja)森林組合法 *Forestry Cooperatives as organizer of public promotion girls no longer exist.
8. Municipal level Industry Enterprise Cooperatives
The cooperatives organized by local industry companies such as green tea, kimono, or Japanese china makers.
Ryokan Cooperatives (= organized by Japanese style inns in hotspring area) are also included into the Industry Enterprise Cooperatives.
basis law = Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Cooperatives Act (ja)中小企業等協同組合法
9. Shopping street/district level commerce cooperatives
The municipal level federations of the cooperatives are also applicable.
basis law = Shopping District Promotion Association Act (ja)商店街振興組合法
10. LG and Other Sector Joint Venture
In the case of called “the third/fourth sector”, it is judged by stake (participation) share. If referring to the fact that a highly public organization has a 50% or more stake (participation) then applicable.

Even though operated by highly public organizations, the “fake” is not applicable on this website.
Then what is the “fake”?

The most fequently used status(role) word is “Ambassador” in Japan and there are many other “fake” ambassadors.
In such situations, it is necessary to distinguish between genuine and fake.
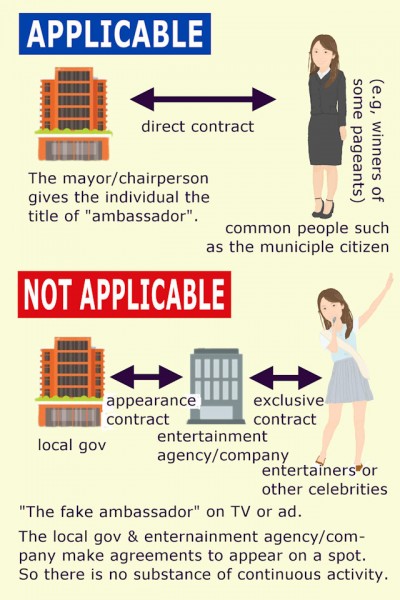
Celebrities (e.g., the entertainer such as singer-dancer(“idol”), rockstar, actress, or writer, commentator, athlete, ..) who will be appointed as “ambassador”s as part of the entertainment business work under an entertainment agreement via entertainment business agency company – They appear on mass media with stage/pen/pseudonym name.
Newspapers/TVs often report that he/she was appointed ambassador. However, the substance is nothing more than an entertainment business contract to appear in advertisements and broadcast programs.
So, on this website, only applicable if the contract is directly with an individual (with real name, not pseudonym name).
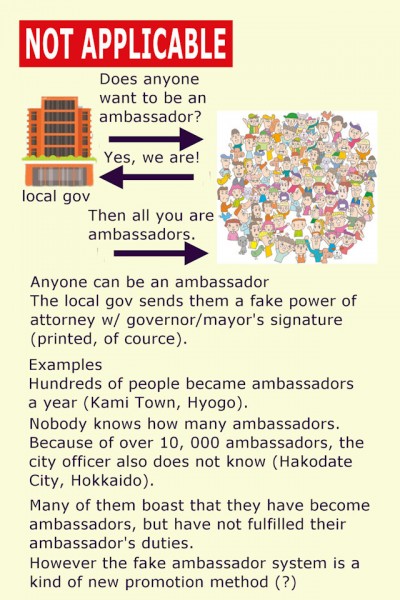
The method “anyone can be an ambassador” in some municipals/prefs is not applicable because most “ambassadors” in the method don’t work as ambassadors (i.e., most of them just boast of their title).

Even if the mayor/chairman claims to be a formal and official “ambassador” title, this website will not accept such “non-human object ambassador”.
Anyway. Many public beauty pageants have been abolished by the gender liberation movement, but a certain number still remain.
In some of them, words such as “Miss” that limit single women are removed from the title and replaced with other titles.
They have almost the same role and purpose as the “local miss”, but they cannot be collectively called the “local miss pageants” because they have different titles. That’s why they can only be called promotion girls(boys).
We are not sure about old pageants in Japan before 2015 though, we presume that many titles consisted of the status name “Miss” plus “Place name” or “Miss” plus “Local special product name”.
Currently, the status/role part of the title “Miss” is often replaced with another word so that it is not limited to single women such as “Queen”, “Princess”, “Belle”, “Lady” and so on. But, the gender-equality issue of targeting only women remains.
So there are also many gender-independent status/role part of the titles such as “Staff”, “Crew”, “Assistant” and so forth. However, you may not feel that high status or authority from such titles.
Then the word for status/role part of the title “ambassador” was developed to solve both “gender” and “authority” issues, we guess.

Initially, it was used as a word that did not deviate from the original meaning of the word “ambassador” as “a person who was entrusted with the work of the promotion (for tourism resources or local products) by a great person (such as mayor/governor of local gov)”.
In other words, the title “ambassador” is still used in that (original; correct) sense by highly public organizations.

However, some private companies (especially promotional companies) are increasingly appointing entertainers appointed to appear in their advertisements or TV programs as “ambassadors.”
Also, some unknown people who want to become celebrities may call themselves “ambassador” without any agreements. In addition, entertainment agencies often want their unnamed entertainers to use the title of “ambassador” because they want to get jobs in advertising.
As a result, in many advertising/entertainment industries, “ambassador” has exactly the same meaning as “promo girl (boy)” and does not necessarily mean high status nor authority in Japan (and some around countries) today.
Therefore, this website covers all real “public” promotion girls/boys (includes all public local miss) in Japan, although, this does not cover all “ambassadors” in Japan.
By the way, what does the “ambassador” mean in your country, now? Does that mean only a high official assigned abroad?
Feb 13, 2021
Kanko of tourism.official.jp (former tourism.lady.jp)
